| .idea | ||
| docs | ||
| examples | ||
| riscemu | ||
| test | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| test.asm | ||
RISC-V (userspace) emulator in python
Implementing a basic RISC-V emulator, aimed at being easily extendable.
This emulator contains:
- RISC-V Assembly parser
- RISC-V Assembly loader
- Emulation for parts of the basic RISC-V instruction set
- Naive memory emulator
- Basic implementation of some syscalls
- A debugging environment
Running simple Assembly:
A couple of basic assembly programs are provided inside examples/, such as hello-world.asm.
You can run it by typing python -m riscemu examples/hello-world.asm. It will produce output similar to:
Successfully loaded: LoadedExecutable[examples/hello-world.asm](base=0x00000100, size=24bytes, sections=data text, run_ptr=0x00000110)
Hello world
Program exited with code 0
See the docs on asembly for more detail on how to write assembly code for this emulator. See the list of implemented syscalls for more details on how to syscall.
Currently, symbols (such as main:) are looked-up at runtime. This allows for better debugging, I believe.
Basic IO should work, as open, read, write and close are supported for stdin/stdout/stderr and even aribtrary file paths (if enabled)
Using the CLI:
Current CLI is not final, options may change frequently until a stable version is reached
This is how the interface is used:
riscemu [--options OPTIONS] [--syscall-option SYSCALL_OPTIONS] [--default_stack_size] file.asm [file.asm ...]
OPTIONS and SYSCALL_OPTIONS is a list of comma-separated flags that will be enabled
OPTIONS:
disable_debug Disable the ebreak and sbreak instructions
no_syscall_symbols Don't make syscall symbols globally available
fail_on_ex Do not launch an interactive debugger when the CPU loop catches an exception
SYSCALL_OPTIONS:
fs_access Allow access to the filesystem
disable_io Disallow reading/writing from stdin/stdout/stderr
If multiple files are specified, all are loaded into memeory, but only the last one is executed. This might be improved
later, maybe the _init section of each binary is executed before the main loop starts?
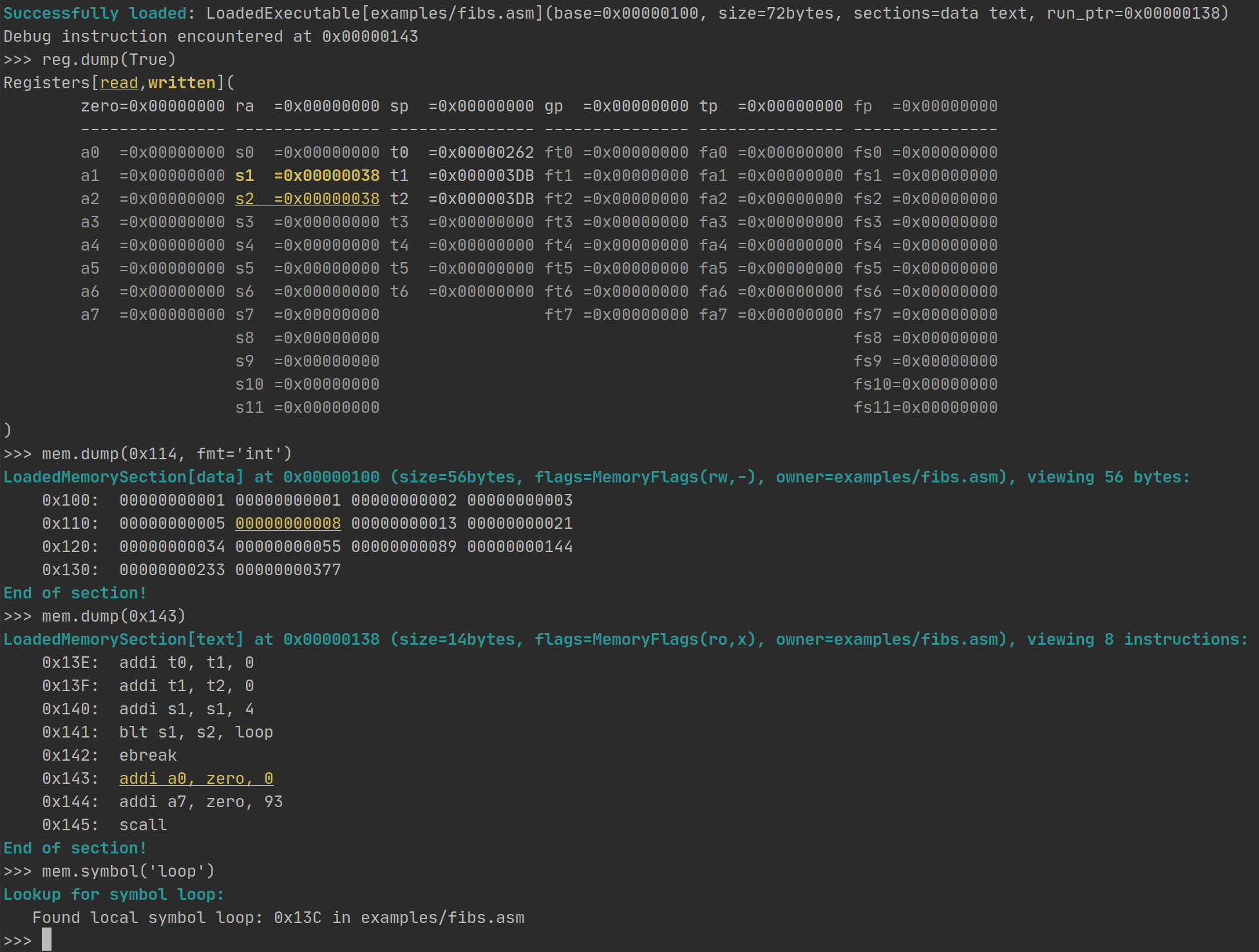
Debugging
Debugging is done using the ebreak (formerly sbreak) instruction, which will launch a debugging session if encountered.
See docs/debugging.md for more info.
Resources:
- Pseudo ops: https://www.codetd.com/article/8981522
- detailed instruction definition: https://msyksphinz-self.github.io/riscv-isadoc/html/rvi.html#add
- RISC-V reference card: https://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/teaching/1617/ECAD+Arch/files/docs/RISCVGreenCardv8-20151013.pdf
TODO:
- Add a cycle limit to the options and CPU to catch infinite loops
- Move away from
printand uselogging.loggerinstead